An open platform for understanding Australia’s methane emissions
Open Methane is an online platform for monitoring Australia’s methane emissions using a combination of atmospheric modelling and satellite measurements.
Explore Methane MapOpen Methane analysis reveals Australia’s top twenty methane hotspots
The early evidence suggests significant underestimation of methane emissions from fossil fuel sites.
Explore the List
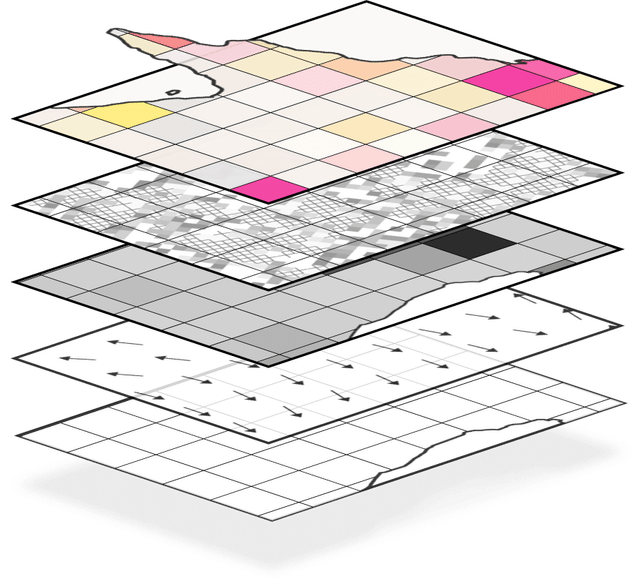
Methodology Overview
View Full Methodology View Full Methodology
Overview
Coming Soon
Open Methane — Full Version
Australian methane map
New map features will allow users to search and filter methane emissions by time, places of interest, land use, trends and events.

Data visualisation tool
Make your own graphs and visualisations of Open Methane data for easy comparison and communication.

Alerts and saved views
Sign up to receive methane event alerts in areas that interest you, and monitor methane activity in specific locations through saved views.